Tired of eating the same old veggies? Stuck with boring Broccoli and predictable salads that make mealtime feel like a chore?
Kitchens everywhere suffer from this vegetable monotony, leaving taste buds craving something new and exciting to spice up their plates.
The good news? A world of tasty vegetables starts with the letter S.
From well-known spinach to weird and wonderful shiso, this list will change how people think about greens.
Forget bland side dishes and menu boredom – there’s a whole garden of flavors waiting to be explored and enjoyed.
Buckle up for a trip through this extensive list of vegetables that start with S. Learn about their tastes, where they
Common Vegetables that Start with S
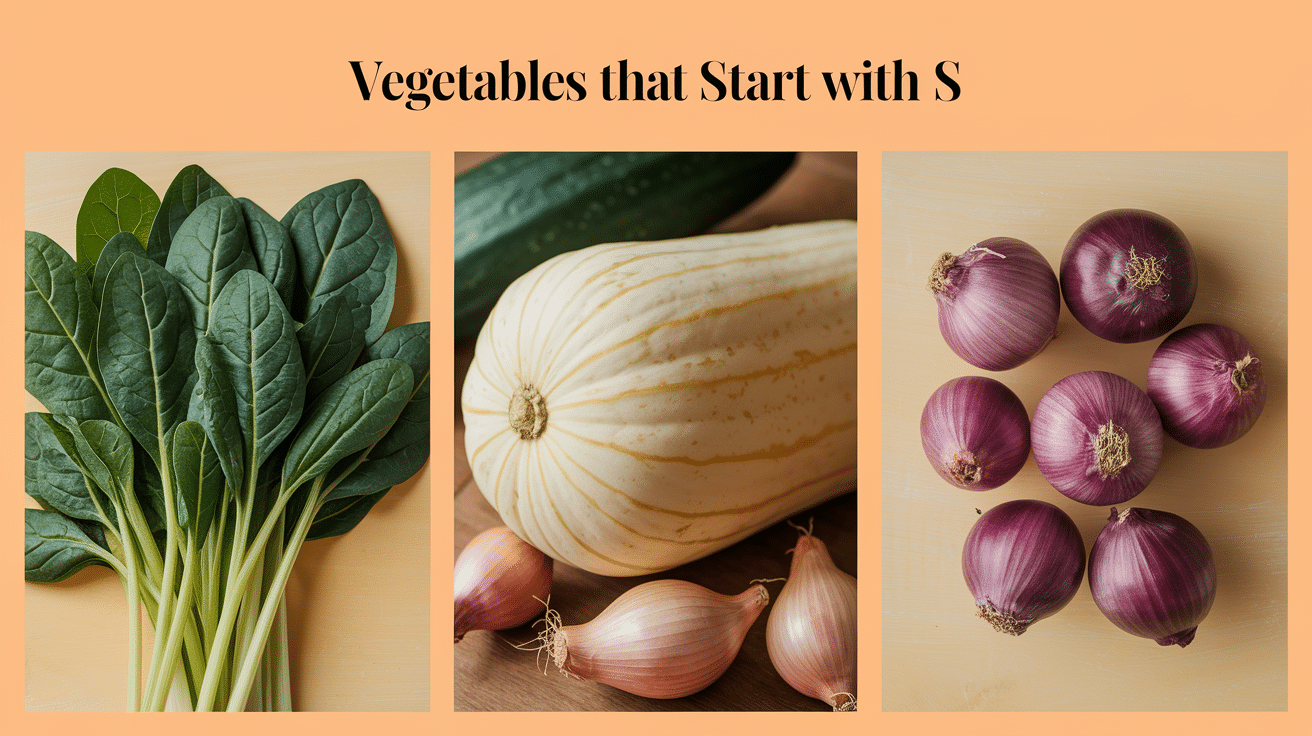
1. Spinach

Scientific Name: Spinacia Oleracea
Origin: Native to Persia (modern-Day Iran) and Has Been Cultivated Worldwide, Especially in Temperate Climates.
Taste: Mildly Sweet and Earthy, with A Tender Texture that Becomes More Flavorful when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Lutein for Eye Health. – Rich in Iron for Healthy Blood. – Packed with Folate for Cell Growth. – Contains Nitrates to Support Blood Flow. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Smoothies, Soups, Stir-Fries, or Eaten Raw as A Garnish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Early Spring to Late Fall. |
2. Sweet Potato

Scientific Name: Ipomoea Batatas
Origin: Native to Central and South America, Particularly in Areas Like Mexico and Peru.
Taste: Sweet, Creamy, and Slightly Nutty with A Smooth Texture when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin A, Supporting Eye Health. – Rich in Fiber for Digestive Health. – Packed with Antioxidants, Particularly Beta-Carotene. – Contains Potassium, Supporting Heart Health. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Casseroles, Roasted, Mashed, or As Fries; Also Used in Desserts. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in The Fall, but Can Be Grown Year-Round in Warm Climates. |
3. Squash

Scientific Name: Cucurbita Spp.
Origin: Native to The Americas, Particularly Cultivated in North, Central, and South America.
Taste: Mild, Slightly Sweet, with A Creamy Texture when Cooked, with Variations Depending on The Type (e.G., Zucchini, Butternut, Acorn).
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin A, Supporting Eye Health. – Rich in Fiber, Aiding Digestion. – Packed with Antioxidants, Particularly Carotenoids. – Contains Potassium, Helping Regulate Blood Pressure. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Stews, Roasted, or Baked; Also Used in Salads and Stir-Fries. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Summer to Fall, Depending on The Variety. |
4. Scallions

Scientific Name: Allium Fistulosum
Origin: Native to Asia, Particularly in Regions Like China and Japan, and Widely Cultivated Around the World.
Taste: Mild and Slightly Sweet, with A Hint of Onion Flavor, Often Used to Add a Fresh Crunch in Dishes.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Contains Sulfur Compounds that May Help Lower Blood Pressure and Support Heart Health. – High in Quercetin, a Flavonoid that May Have Anti-Inflammatory and Immune-Boosting Properties. – Rich in Prebiotic Fiber, Promoting Gut Health by Supporting Beneficial Bacteria. – a Source of Vitamin K, Which Supports Bone Health and Proper Blood Clotting. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Stir-Fries, Soups, as A Garnish, or Eaten Raw in Sandwiches and Tacos. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Early Spring to Late Summer. |
5. Snow Peas

Scientific Name: Pisum Sativum
Origin: Native to The Mediterranean Region and Widely Cultivated in Temperate Climates Around the World.
Taste: Sweet and Crunchy with A Mild Flavor, Often Eaten Raw or Lightly Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Rich in Vitamin C, Supporting Immune Health and Skin Vitality. – Contains Saponins, Which Have Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. – High in Folate, Which Is Important for Cell Growth and Regeneration. – Provides a Good Source of Iron, Helping Prevent Anemia and Supporting Energy Levels. |
| Common Uses | Eaten Raw in Salads, Stir-Fried, or Added to Soups and Stews. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Early Spring to Early Summer. |
6. Swiss Chard

Scientific Name: Beta Vulgaris
Origin: Native to The Mediterranean Region, Commonly Found in Europe, Asia, and North America.
Taste: Mildly Earthy and Slightly Sweet, with Thick, Tender Leaves and Crunchy Stems.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Rich in Betalains, Which Are Antioxidants that Help Reduce Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. – High in Magnesium, Which Supports Muscle and Nerve Function. – Contains Vitamin K, Essential for Bone Health and Blood Clotting. – Provides Potassium, Which Helps Regulate Blood Pressure. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Salads, Sautéed, or As a Side Dish; Often Used as A Substitute for Spinach or Kale. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Spring to Early Fall, but Can Be Grown Year-Round in Mild Climates. |
7. Shallots

Scientific Name: Allium Cepa var. Cepa
Origin: Native to Central or Southwest Asia, Commonly Cultivated in Europe and The Middle East.
Taste: Mild and Sweet, with A More Delicate Flavor than Onions, Slightly Garlicky with A Hint of Sharpness.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Contains Allyl Propyl Disulfide, Which May Help Reduce Cholesterol Levels and Support Heart Health. – Rich in Antioxidants, Especially Quercetin, Which May Help Reduce Inflammation. – High in Prebiotic Fiber, Which Nourishes Beneficial Gut Bacteria and Supports Digestive Health. – Provides Manganese, Supporting Bone Health and The Metabolism of Nutrients. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Dressings, Sauces, Soups, Stir-Fries, and As a Garnish for Various Dishes. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Spring to Early Summer, Depending on The Growing Region. |
8. Snap Peas

Scientific Name: Pisum Sativum var. Macrocarpon
Origin: Native to The Mediterranean Region, but Now Widely Cultivated in Temperate Climates Across the Globe.
Taste: Sweet and Crunchy, with A Smooth, Edible Pod that Provides a Fresh, Garden-Like Flavor when Eaten Raw or Lightly Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin K, Which Is Essential for Bone Health and Proper Blood Clotting. – Rich in Lutein, Supporting Eye Health and Reducing the Risk of Age-Related Vision Loss. – Contains Saponins, Which May Have Anti-Inflammatory and Immune-Boosting Effects. – a Good Source of Folate, Which Is Important for Cell Growth and Regeneration. |
| Common Uses | Eaten Raw in Salads, Stir-Fried, Steamed, or Added to Soups and Casseroles. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Early Spring to Late Summer, Depending on The Region. |
9. Sweet Corn

Scientific Name: Zea Mays
Origin: Native to Central America, Particularly Mexico, and Has Been Cultivated by Indigenous People for Thousands of Years.
Taste: Sweet, Juicy, and Tender with A Mild Starchy Flavor, Particularly when Freshly Picked or Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Antioxidants, Particularly Lutein and Zeaxanthin, Which Support Eye Health and Protect Against Macular Degeneration. – Rich in Fiber, Which Aids Digestion and Helps Maintain Stable Blood Sugar Levels. – Contains Vitamin B6, Which Plays a Role in Brain Function and The Production of Red Blood Cells. – Provides a Good Source of Magnesium, Supporting Muscle Function and Overall Body Health. |
| Common Uses | Eaten Boiled or Grilled on The Cob, Used in Soups, Salads, Salsas, or Made Into Cornmeal for Baking. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Summer to Early Fall. |
10. Soybeans

Scientific Name: Glycine Max
Origin: Native to East Asia, Particularly in Regions Like China and Japan.
Taste: Mildly Nutty and Slightly Sweet, with A Firm Texture when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Plant-Based Protein, Making It an Excellent Choice for Vegetarians and Vegans. – Rich in Isoflavones, Which May Help Regulate Hormonal Balance. – Contains Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Supporting Heart Health. – Provides Iron, Which Helps Prevent Anemia and Supports Energy Levels. |
| Common Uses | Used in Tofu, Tempeh, Edamame, Soy Milk, or Ground Into Flour. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Summer to Early Fall. |
11. Salsify

Scientific Name: Tragopogon Porrifolius
Origin: Native to Europe and Parts of Asia, Commonly Grown in Temperate Climates.
Taste: Slightly Sweet and Nutty, with A Flavor Similar to Oysters when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Rich in Inulin, a Prebiotic Fiber that Supports Gut Health by Nourishing Beneficial Bacteria. – High in Potassium, Which Helps Regulate Blood Pressure. – Contains Antioxidants Like Flavonoids that Reduce Oxidative Stress. – a Good Source of Vitamin C, Boosting Immune Function. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Stews, Roasted, or As a Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Fall to Early Winter. |
12. Shiso

Scientific Name: Perilla Frutescens
Origin: Native to East Asia, Particularly Japan, Korea, and China.
Taste: Aromatic with A Flavor that Combines Basil, Mint, and A Hint of Anise, Often Used in Japanese Cuisine.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Contains Rosmarinic Acid, Which Has Anti-Inflammatory Properties and Supports Respiratory Health. – High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Promoting Heart Health. – Rich in Vitamin A, Supporting Eye Health and Immune Function. – Contains Iron and Calcium, Aiding Blood Health and Bone Strength. |
| Common Uses | Used in Sushi, Salads, Pickles, and Garnishes. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in The Summer Months. |
13. Savoy Cabbage

Scientific Name: Brassica Oleracea var. Sabellica
Origin: Native to Europe, Especially the Mediterranean Region, and Widely Cultivated Across Temperate Climates.
Taste: Milder and Sweeter than Regular Cabbage, with Crinkled Leaves and A Tender Texture.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin K, Which Supports Bone Health and Blood Clotting. – Rich in Glucosinolates, Which May Have Anti-Cancer Properties. – Contains Fiber, Promoting Digestive Health. – a Good Source of Folate, Which Supports Cell Growth and Regeneration. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Salads, Stir-Fries, or Stuffed in Rolls. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Fall to Early Winter. |
14. Sesame Leaves

Scientific Name: Sesamum Indicum
Origin: Native to India and Africa, and Widely Cultivated in Tropical Regions.
Taste: Earthy, Slightly Nutty, and Peppery, with A Rich Aromatic Flavor.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Antioxidants, Particularly Sesamin, Which Supports Liver Health. – Rich in Calcium, Which Supports Bone Health. – Contains Vitamin E, Which Supports Skin Health and Acts as An Antioxidant. – Provides Magnesium, Supporting Muscle Function and Relaxation. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, as Wraps, or In Soups and Stews. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in The Summer to Fall. |
15. Sorrel

Scientific Name: Rumex Acetosa
Origin: Native to Europe and Parts of Asia, Commonly Found in Temperate Regions.
Taste: Tangy and Sour, Similar to Lemon, with A Sharp, Refreshing Flavor.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin C, Boosting the Immune System and Supporting Skin Health. – Contains Oxalates, Which May Help Detoxify the Body and Promote Kidney Health. – Rich in Potassium, Helping Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure. – a Good Source of Iron, Which Supports Energy and Red Blood Cell Formation. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Salads, Sauces, and As a Garnish in Various Dishes. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Spring to Early Summer. |
16. Sugar Snap Peas

Scientific Name: Pisum Sativum var. Macrocarpon
Origin: Native to The Mediterranean Region, Now Widely Cultivated Around the World.
Taste: Sweet, Crunchy, and Slightly Earthy with A Tender Pod that Can Be Eaten Whole.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin K, Supporting Bone Health. – Contains a Significant Amount of Folate, Which Is Essential for Cell Division. – Rich in Antioxidants Like Flavonoids, Reducing Inflammation. – Provides Plant-Based Protein, Supporting Muscle Growth and Repair. |
| Common Uses | Eaten Raw, Added to Salads, Stir-Fries, or Steamed as A Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Early Spring to Late Summer. |
17. Shiitake Mushrooms

Scientific Name: Lentinula Edodes
Origin: Native to East Asia, Particularly Japan, China, and Korea.
Taste: Earthy, Savory, and Umami, with A Meaty Texture when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Contains Lentinans, Which May Support Immune Function. – Rich in B Vitamins, Promoting Energy Metabolism. – High in Copper, Which Helps with The Production of Red Blood Cells. – Contains Polysaccharides, Which Are Believed to Have Anti-Inflammatory Properties. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Stir-Fries, Sauces, or Sautéed as A Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in The Fall to Early Winter. |
18. Sunflower Shoots

Scientific Name: Helianthus Annuus
Origin: Native to North America, Now Grown Worldwide for Culinary and Nutritional Uses.
Taste: Fresh, Nutty, and Slightly Peppery with A Tender Crunch.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin E, Which Supports Skin Health and Acts as An Antioxidant. – Rich in Zinc, Promoting a Healthy Immune System. – Contains Chlorophyll, Which May Support Detoxification. – Provides Essential Fatty Acids that Support Heart Health. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Sandwiches, or As a Garnish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Spring to Summer. |
19. Sweet Pepper

Scientific Name: Capsicum Annuum
Origin: Native to The Americas, Particularly Cultivated in Central and South America.
Taste: Sweet, Mild, and Juicy with A Crunchy Texture, Varying in Flavor from Green to Red as It Ripens.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin C, Supporting Immune Health. – Contains Capsaicin, Which May Aid Metabolism and Fat Burning. – Rich in Antioxidants Like Carotenoids, Promoting Eye Health. – a Good Source of Fiber, Supporting Digestive Health. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Stir-Fries, Stuffed, or As a Topping for Various Dishes. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Summer to Early Fall. |
20. Siberian Kale

Scientific Name: Brassica Oleracea var. Sabellica
Origin: Native to Europe, Particularly in The Cold Regions of Siberia.
Taste: Earthy and Slightly Bitter, with A More Tender Texture than Other Kale Varieties.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin C, Supporting Immune Health. – Contains Anthocyanins, Which Are Antioxidants that Help Reduce Inflammation. – Packed with Iron, Which Supports Blood Health. – Rich in Magnesium, Which Supports Muscle and Nerve Function. |
| Common Uses | Used in Soups, Stews, Stir-Fries, or Sautéed as A Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Fall to Early Winter. |
21. Sweet Onion

Scientific Name: Allium Cepa
Origin: Developed in The United States, Particularly in Regions Like California.
Taste: Mild, Sweet, and Juicy with A Light, Non-Pungent Flavor.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Contains Antioxidants, Such as Quercetin, Which Support Heart Health. – Rich in Sulfur Compounds, Which May Help Lower Blood Pressure. – High in Vitamin C, Supporting Skin Health and Immunity. – Contains Prebiotics that Support Gut Health. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Sandwiches, Grilled, or In Soups and Sauces. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in The Summer Months. |
22. Samphire

Scientific Name: Salicornia Europaea
Origin: Native to Coastal Areas of Europe, North America, and Asia, Typically Found in Salt Marshes and Along the Seashore.
Taste: Crisp, Salty, and Slightly Briny with A Fresh, Tangy Flavor, Often Compared to Sea Vegetables Like Seaweed.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Iodine, Supporting Thyroid Function and Metabolism. – Rich in Antioxidants Like Flavonoids, Which Help Reduce Inflammation. – Contains Vitamin K, Which Supports Bone Health and Proper Blood Clotting. – Provides a Good Amount of Calcium, Supporting Strong Bones and Teeth. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Stir-Fries, as A Garnish, or Served with Fish and Seafood Dishes. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Spring to Early Fall when It Is Most Tender. |
23. Spaghetti Squash

Scientific Name: Cucurbita Pepo
Origin: Native to North and South America, Widely Cultivated in Temperate Regions.
Taste: Mildly Sweet and Slightly Nutty with A Fibrous, Spaghetti-Like Texture when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Low in Calories and High in Water Content, Promoting Hydration. – Rich in Fiber, Supporting Digestive Health. – High in Antioxidants Like Beta-Carotene, Promoting Eye Health. – Contains Vitamin C, Which Supports the Immune System. |
| Common Uses | Used as A Pasta Substitute, Roasted, in Soups, or As a Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Summer to Early Fall. |
24. Stinging Nettles

Scientific Name: Urtica Dioica
Origin: Native to Europe, Asia, and North America, Commonly Found in Temperate Climates.
Taste: Earthy and Slightly Grassy, with A Mild Bitterness, Particularly when Cooked.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – Rich in Iron, Helping with Energy Levels and Red Blood Cell Production. – Contains Silica, Which Supports Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails. – High in Antioxidants, Particularly Flavonoids, Which Reduce Inflammation. – Provides Vitamin K, Supporting Bone Health. |
| Common Uses | Used in Teas, Soups, Stews, or Sautéed as A Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Early Spring Before Flowering. |
25. Sweet Italian Pepper

Scientific Name: Capsicum Annuum
Origin: Native to The Americas, Especially Cultivated in Regions Like Italy for Sweet Pepper Varieties.
Taste: Sweet, Mild, and Juicy with A Slightly Tangy Flavor, Often Larger and More Fleshy than Other Peppers.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Benefits | – High in Vitamin C, Supporting the Immune System. – Contains Capsaicin, Which May Promote Fat Burning. – Rich in Antioxidants Like Carotenoids, Promoting Skin and Eye Health. – Provides Potassium, Supporting Healthy Muscle and Nerve Function. |
| Common Uses | Used in Salads, Stir-Fries, Stuffed Peppers, or Roasted as A Side Dish. |
| Season | Typically Harvested in Late Summer to Early Fall. |
Lesser Known Vegetables that Start from S
-
Sweet Basil: Native to Southeast Asia, with A Sweet, Aromatic Flavor. Rich in Vitamin K, Antioxidants, and Supports Digestion and Heart Health.
-
Sea Buckthorn: A Bright Orange Berry from Coastal Regions, Packed with Vitamin C, Antioxidants, and Omega-7, Supporting Skin Health and Immune Function.
-
Salsa Lettuce: A Crisp, Mild-Tasting Lettuce Variety, Often Used in Salads. It’s High in Fiber, Vitamin A, and Provides Hydration with A Low-Calorie Count.
-
Sorghum: A Drought-Tolerant Grain with High Fiber and Protein Content. It Supports Digestion, Heart Health, and Is Rich in Antioxidants.
-
Shungiku (chrysanthemum Leaves): Popular in East Asian Cuisine, with A Slightly Bitter Taste. It’s Rich in Vitamins A, C, and Iron, Promoting Immune Health.
-
Scorzonera: Also Known as Black Salsify, It Has an Earthy, Sweet Flavor. Rich in Inulin, Potassium, and Vitamin B6, Supporting Digestive Health.
-
Salsola (also Known as Glasswort): A Succulent Plant with A Salty Flavor, Often Used in Salads or Pickled. High in Vitamin C and Minerals Like Calcium.
-
Shiro Miso: A Fermented Soybean Paste with A Sweet, Mild Flavor. It’s Rich in Protein, Probiotics, and Helps Promote Gut Health.
-
Snake Gourd: A Long, Slender Vegetable with A Mild Taste. It’s Rich in Vitamin C, Potassium, and Fiber, Promoting Digestive Health.
-
Spigarello: A Leafy Green Related to Broccoli, with A Slightly Bitter Taste. It’s High in Vitamins C and K, Supporting Immunity and Bone Health.
-
Solomon’s Seal: An Herb with Edible Roots, Used in Traditional Medicine. Rich in Antioxidants and Anti-Inflammatory Compounds, Supporting Joint and Digestive Health.
-
St. John’s Wort (young Leaves): Known for Its Medicinal Properties, Especially for Mood Regulation. Contains Antioxidants and Compounds Supporting Mental Wellness.
-
Smoked Tomato: A Tomato Variety with A Smoky Flavor, Rich in Lycopene, Antioxidants, and Vitamin C, Supporting Skin Health and Immunity.
-
Snow Cabbage: A Hardy Cabbage Variety, Known for Its Mild Flavor. High in Vitamin C, Fiber, and Calcium, Supporting Immune Health and Digestion.
-
Saltwort: A Coastal Plant with A Salty Flavor, High in Vitamin C, Calcium, and Iron, Promoting Skin Health and Bone Strength.
-
Skirret: A Root Vegetable with A Sweet Flavor, High in Inulin, Which Aids Digestion. It Also Provides Potassium and Vitamin C.
-
Salad Burnet: A Herb with A Mild, Cucumber-Like Taste. High in Vitamin C, Antioxidants, and Beneficial for Digestive Health and Skin Rejuvenation.
-
Spicy Radish: A Root Vegetable with A Peppery Taste. Rich in Vitamin C, Fiber, and Antioxidants, Supporting Immunity and Digestive Health.
-
Sunroot (jerusalem Artichoke): A Tuber with A Sweet, Nutty Flavor. High in Inulin, Supporting Gut Health, and Rich in Iron and Potassium for Energy.
-
Sweet Lemon Cucumber: A Cucumber Variety with A Mild, Citrus-Like Flavor. Rich in Water, Vitamin C, and Antioxidants, Supporting Hydration and Immunity.
-
Sweet Mignonette Lettuce: A Tender, Mild Lettuce Variety, Rich in Vitamin A, Fiber, and Antioxidants, Promoting Eye Health and Digestion.
-
Sweetheart Cabbage: A Tender Cabbage Variety with Sweet, Crisp Leaves. High in Vitamin C, Fiber, and Antioxidants, Supporting Immune and Digestive Health.
-
Seaweed (edible Types Like Nori, Wakame): Rich in Iodine, Calcium, and Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Supporting Thyroid Health and Cardiovascular Function.
-
Shallot Greens: The Leafy Tops of Shallots, with A Mild Onion Flavor. Rich in Vitamins a And C, Supporting Eye Health and Immune Function.
-
Salicornia (marsh Samphire): A Salty Vegetable, Packed with Vitamin C, Calcium, and Antioxidants, Supporting Digestion and Skin Health.
-
Snake Bean: A Long, Thin Bean with A Crisp Texture. High in Fiber, Protein, and Vitamin A, Supporting Digestion and Overall Health.
-
Starfruit (when Used as Vegetable): A Tropical Fruit with A Tangy Flavor, Rich in Vitamin C, Fiber, and Antioxidants, Promoting Immune and Skin Health.
-
Sweet Mallow: A Leafy Green with A Sweet Flavor. High in Vitamin C, Iron, and Calcium, Supporting Skin Health, Iron Levels, and Bone Strength.
-
Sandwich Cucumber: A Mild Cucumber Variety, Ideal for Sandwiches. High in Water, Vitamin K, and Antioxidants, Supporting Hydration and Joint Health.
-
Spanish Onion: A Sweet Onion Variety, High in Antioxidants and Vitamin C, Promoting Heart Health and Reducing Inflammation.
-
Salsify (black Oyster Plant): A Root Vegetable with A Mild, Oyster-Like Flavor. Rich in Potassium, Vitamin B6, and Fiber, Supporting Digestion and Heart Health.
-
Siberian Mustard: A Hardy Mustard Variety with A Spicy Flavor. Rich in Vitamin C, Antioxidants, and Beneficial for Detoxification and Digestion.
-
Sprouted Broccoli: Young Broccoli Shoots, High in Sulforaphane, Which Helps Fight Cancer Cells. Also Packed with Fiber, Vitamin C, and Antioxidants.
-
Spicy Green Beans: Green Beans with A Slight Heat. Rich in Fiber, Vitamin C, and Antioxidants, Supporting Digestion, Immunity, and Heart Health.
-
Silken Tofu (used as A Vegetable Substitute): A Soft, Protein-Rich Alternative to Meat. It Contains Iron, Calcium, and Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Supporting Bone and Heart Health.
-
Sweet Potato Vine Leaves: The Edible Leaves of Sweet Potato Plants, Rich in Vitamin A, Iron, and Calcium, Supporting Vision and Bone Health.
-
Salsify Root: A Root Vegetable with A Mild, Sweet Flavor. Rich in Fiber, Potassium, and Antioxidants, Supporting Digestive and Heart Health.
-
Spineless Cactus (prickly Pear Cactus): The Pads of The Cactus Are Rich in Fiber, Vitamin C, and Antioxidants, Supporting Digestion and Skin Health.
-
Stonecrop (used in Salads): A Succulent Plant, Often Used in Salads. Rich in Vitamin C and Antioxidants, Promoting Skin Health and Immune Function.
-
Shungiku Chrysanthemum: An Herb with Mild Bitterness. Rich in Vitamin A, C, and Antioxidants, Supporting Immune Function and Skin Health.
-
Shepherd’s Purse (wild Edible): A Wild Green with A Peppery Taste. High in Vitamin C, Iron, and Antioxidants, Supporting Immunity and Blood Health.
-
Spring Onion (different from Shallots): A Mild Onion Variety with A Crisp Texture. Rich in Vitamin C and Antioxidants, Supporting Immune Health and Digestion.
-
Sea Lettuce: A Type of Edible Seaweed, High in Iodine, Calcium, and Iron, Promoting Thyroid Function and Bone Strength.
-
Sorghum Greens: The Young Leaves of Sorghum, Rich in Antioxidants, Fiber, and Vitamin A, Supporting Digestion and Eye Health.
- Shallot Greens: Mildly onion-flavored leaves, rich in vitamins A and C, promoting immune health, digestion, and supporting eye health.
Conclusion
Now you know about many vegetables that start with “S”! From common ones like spinach and squash to unusual ones like shiso and skirret, each vegetable is special and good for you in different ways.
Some help make your bones strong, others help your eyes see better, and many help your body fight off sickness.
These vegetables grow in many places around the world – from farms in America to gardens in Asia and wild spots in Europe.
This list shows how many different vegetables there are beyond what we usually see at the store.
Sometimes we get used to eating the same vegetables all the time, but there’s a whole world of tasty options out there.
Who knows – your new favorite vegetable might be waiting for you on this list!